Many factors such as number of vehicles, speed, climatic conditions and other factors affect are to be considered for the design of pavement. In this article we will discuss about the factors influencing pavement design. Pavements are engineered structures which are used as roads, runways, parking areas, etc. Ground or surface transportation is the most widely used transportation in the world. So, construction of pavements should be done as it is strong and durable for their design life.

Fig 1 : Factors Affecting Pavement Design
Factors Affecting Pavement Design
There are so many factors which influencing the pavement design. The factors may be of loading, environment, materials used etc. Which are as follows.
- Wheel load
- Axle configuration
- Contact pressure
- Vehicle speed
- Repetition of loads
- Subgrade type
- Temperature
- Precipitation
1. Wheel Load Influence on Pavements
Wheel load on pavement is an important factor to determine the pavement thickness to be adopted. By providing adequate thickness, the load coming from wheels doesn’t affect the subgrade soil. The wheel load is acts at particular point on pavement and cause deformations. If the vehicle contains dual wheels on one side of axle, then convert it into equivalent single wheel load. Dual wheeled axle vehicles control the contact pressure within the limits.
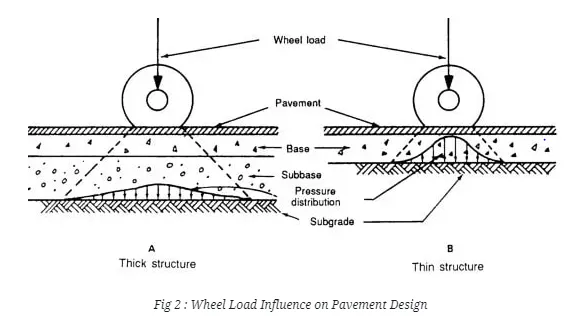
2. Axle Configuration
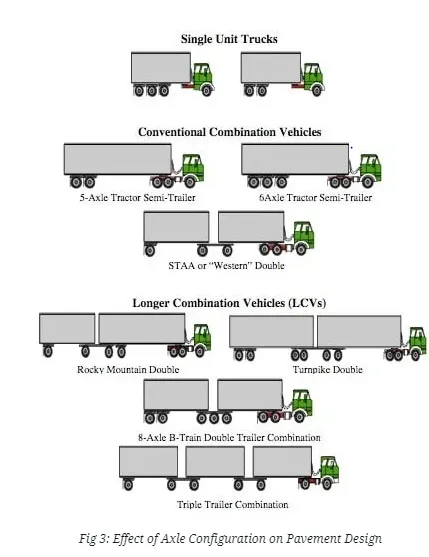
Axles are the important part of the vehicles which enables the wheels to rotate while moving. By providing multiple axles, vehicle can carry more load. So, the axle load also influences the design of pavement. In the layer theory of flexible pavement design wheels on one side of axles are considered to design the pavement. Similarly in the plate theory of rigid pavement design wheels on both sides are considered.
3. Tire Contact Pressure on Pavement
When the vehicle is moving on pavement, a pressure developed between the tire and pavement. If the tire is low pressure tire, then contact pressure will be greater than tire pressure. If it is high pressure tire, then contact pressure will be less than tire pressure. The original Shape of contact area is generally elliptical. But to ease the calculations circular shape is considered.

Fig 4: Tire Contact Pressure on Pavement
4. Vehicle Speed
If the vehicle is moving at creep speed then also damage occurs to the pavement. If vehicle speed is gradually increased then it will cause smaller strains in the pavement.
5. Repetition of Loads
Constructed pavement is used by several vehicles in its design life. The wheel loads are repeated all the time due to this some deformation occurs on the pavement. Total deformation is the sum of all wheel loads acting on it. So, in the design of pavement frequency of load is also considered. For the design of pavement, single axle with dual wheels carrying 80 Kn load is considered as standard axle.
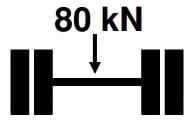
Fig 5: Axle Load on Pavement
6. Subgrade Type
To construct pavement sub grade soil need to be tested. Various test like CBR, Tri axial etc. will helps to determine the quality of subgrade. From this we can adopt the required thickness to the pavement. If subgrade soil is poor then the pavement should damage easily.

Fig 6: Effect of Subgrade Type on Pavement Design
7. Temperature Effects on Pavements Design
Temperature is the important environmental factor to be considered in the design of pavement. In case of asphalt roads, temperature affects the resilient modulus of surface course. In very hot condition asphalt layers lose their stiffness. At low temperature, asphalt layers become brittle and cracks are formed.

Fig 7: Temperature Effects on Pavements Design
In case of rigid pavement, temperature stresses are developed. Curling of concrete is also possible due to variation of temperature in top and bottom layers of pavement.
8. Precipitation

Fig 8: Effect of Rain on Pavement Design
Moisture variations or precipitation from rain affects the depth of groundwater table. Good drainage facilities should be provided for good strength and support. The ground water table should be at least below 1m from the pavement surface.



Comments are closed