Influence lines, which describe variation of any function Z (reaction, bending moment, shear, etc.) in the fixed section due to moving concentrated unit load P D 1 may be effectively used for calculation of this function Z due to arbitrary fixed and moving loads.
Fixed Loads
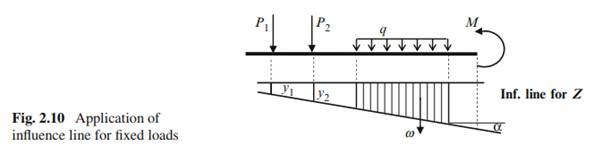
Three types of fixed loads will be considered: concentrated loads, uniformly distributed loads, and couples as shown in Fig. 2.10. Let us consider effect of each load separately
Concentrated Loads

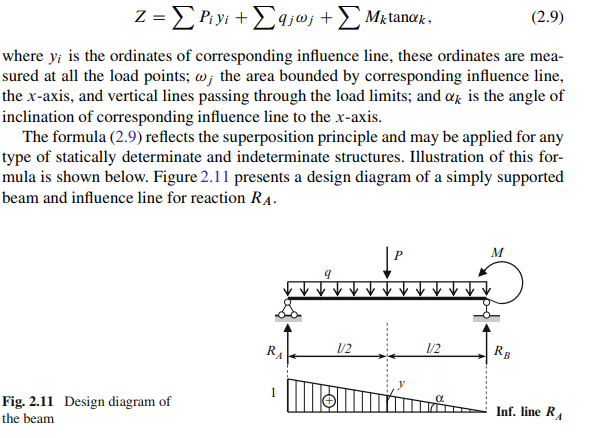
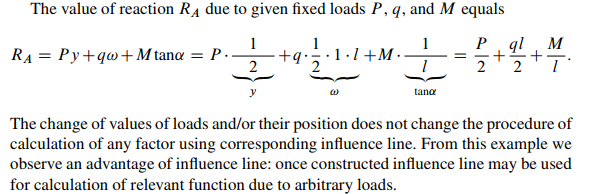
In order to compute the value of any function (reaction, internal forces in any section of the beam, frame, or any member of the truss, etc.) arising under the action of several concentrated loads Pi , the corresponding influence line must be constructed, each load should be multiplied by the ordinate of the influence line measured at the load point, and the obtained products must be summed up.
It is easy to check that units of ordinate of influence lines, which have been discussed early, lead to the required units for function Z.
Uniformly Distributed Load
Value of any function Z due to action of uniformly distributed load q is determined by formula Z D ˙q!, with ! the area of influence line graph for function Z within the portion where load q is applied. If the influence line within the load limits has different signs then the areas must be taken with appropriate signs. The sign of the area coincides with sign of ordinates of influence line.
Couple
If a structure is loaded by couple M, then function Z, due to this moment is Z D ˙ M tan˛, where ˛ is the angle between the base line and the portion of influence line for function Z within which M is applied. If couple tends to rotate influence line toward base line through an angle less than 90 then sign is positive; if angle is greater then 90 then sign is negative.
Summary
Influence line for any function may be used for calculation of this function due to arbitrary fixed loads. In a general case, any function Z as a result of application of a several concentrated loads Pi , uniform loads intensity qj , and couples Mk should be calculated as follows: