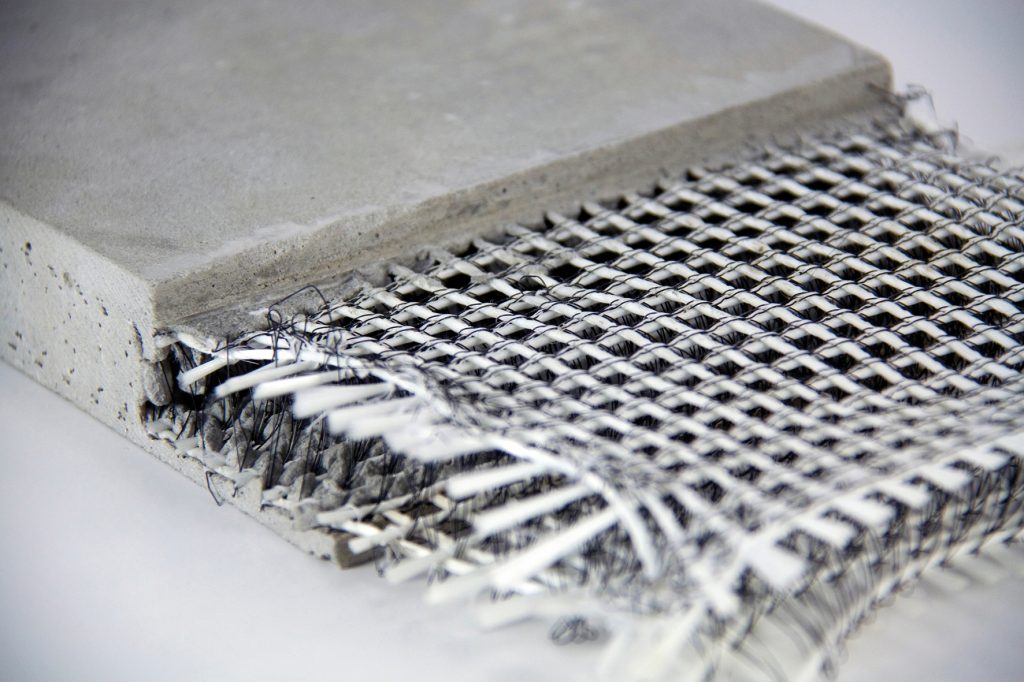
Plain concrete possesses deficiencies like low tensile strength, limited ductility and low resistance to cracking. The cracks develop even before loading. After loading micro cracks widen and propagate, exposing concrete to atmospheric actions. If closely spaced and uniformly dispered fibres are provided while mixing concrete, cracks are arrested and static and dynamic properties are improved. Fibre reinforced concrete can be defined as a composite material of concrete or mortar with discontinuous
and uniformly distributed fibres. Commonly used fibres are of steel, nylon, asbestos, coir, glass, carbon and polypropylene. The length to lateral dimension of fibres range from 30 to 150. The diameter of fibres vary from 0.25 to 0.75 mm.
Fibre reinforced concrete is having better tensile strength, ductility and resistance to cracking.
Uses of FRC
1. For wearing coat of air fields, roads and refractory linings.
2. For manufacturing precast products like pipes, stairs, wall panels, manhole covers and boats.
3. Glass fibre reinforced concrete is used for manufacturing doors and window frames, park
benches, bus shelters etc.
4. Carbon FRC is suitable for structures like cladding and shells.
5. Asbestos FRC sheets are commonly used as roofing materials.