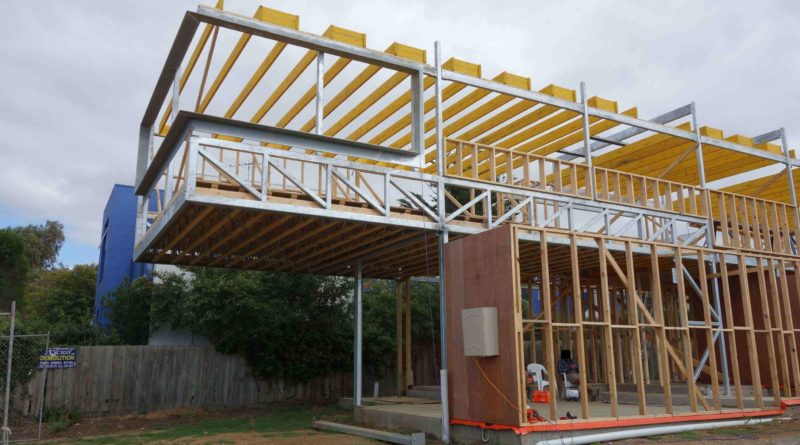
Trusses are the frame formed by number of straight members connected in the form of triangles
The embers are made by steel angles and they are joined by rivet or welding, these joints are called nodes
It is assumed that the external loads act at the nodes only and the members are subjected to only tension or compression
The compression members are called as struts and the tension members are called as ties
Steel roof trusses are used under the following condition
Large spans are to be covered
Intermediate columns are to be avoided to have an unobstructed working area inside
There is a heavy rain or snow fall
Types of roof trusses
King post truss
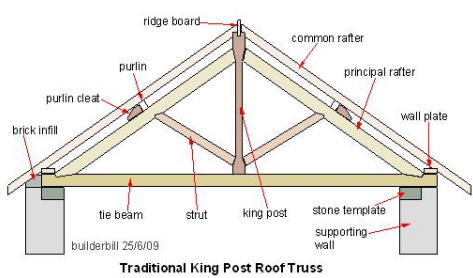
Here the common rafters are supported by wooden frame work called truss under required interval
The frame work consist of a king post, two struts two principal rafters and tie beam
The truss rest on stone bed blocks at either end
The common rafters rest on wooden purlins which in turn are fixed to the principal rafters of the truss
The king post connect the ridge post and the middle of the tie beam
The struts are connected to the king post at the bottom and the principal rafters at the top
The roofing material is fixed to the common rafters king post truss is used for spans of 5m to 9m
Queen post truss
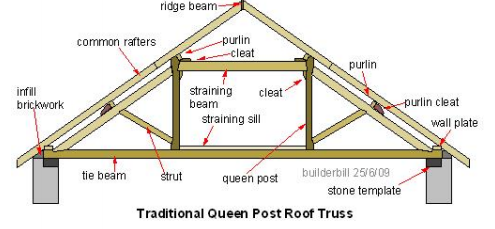
The frame work consist of two principal rafters ,two queen post one straining sill two struts one tie beam and one straining beam.
The common matters rest on wooden purlins
The staining beam resist the horizontal thrust developed
The struts are connected to the queen post at the bottom and the principal rafters at the top
North light roof truss
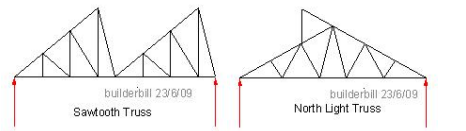
North light or saw tooth roof truss is special type of roof trusses suitable for factories engaging in manufacturing work
North light truss is sawtooth
Actual lighting is taken an advantage during day time by using the north light roof trusses In this type of trusses vertical drops are provided this drops are covered with glasses so as to permit light in to the interior
Centering and shuttering
Shuttering is the temporary ancillary construction used as a mould for the structures In which the concrete is placed and allowed to hardened
These are classified as steel wooden plywood combined woods steel, reinforced concrete and plain concrete
Requirements of shuttering The material should be cheap and should be suitable for re use several times
It should be practically water proof so that it should not observe water from concrete
It should be strong enough to with stand all loads coming on it
It should be stiff enough so that deflection is minimum
The surface of the formwork should smooth and it should afford easy stripping
Loads on form work
Live load due to labour etc
Dead weight of wet concrete
Hydrostatic pressure of the fluid concrete
Impact due t pouring concrete
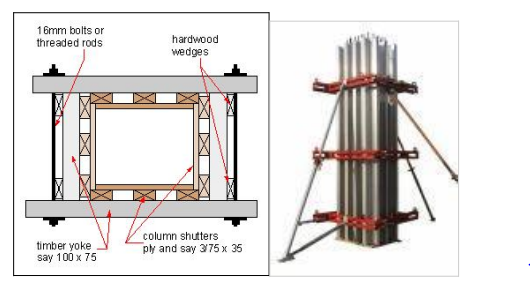
Shuttering for column
Components
Sheeting or column shutter all around the column
Yokes
Wedges
Bolt
Shuttering for beam and slab floor
The slab is continous over the beam
The slab is supported on 2.5 cm thick sheeting laid parallel to the main beam
The boarding may be 4 to 5 cm thick for walls up to 3to 4m high
The boards are fixed to 5cmX10cm posts known as struts are soldiers.


