Posted inAdvanced
Posted inSurveying
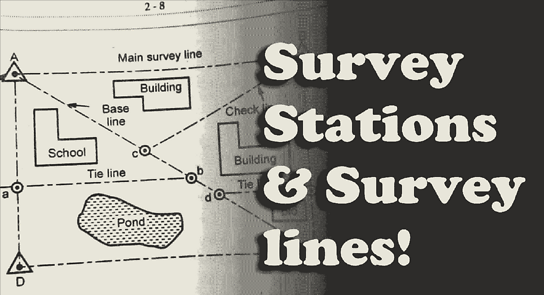
Selection of Stations
The following points should be considered in selecting station points: (i) It should be visible…
Posted inSurveying
Technical Terms
Various technical terms used in connection with the network of the triangles in surveying are…
Posted inSurveying
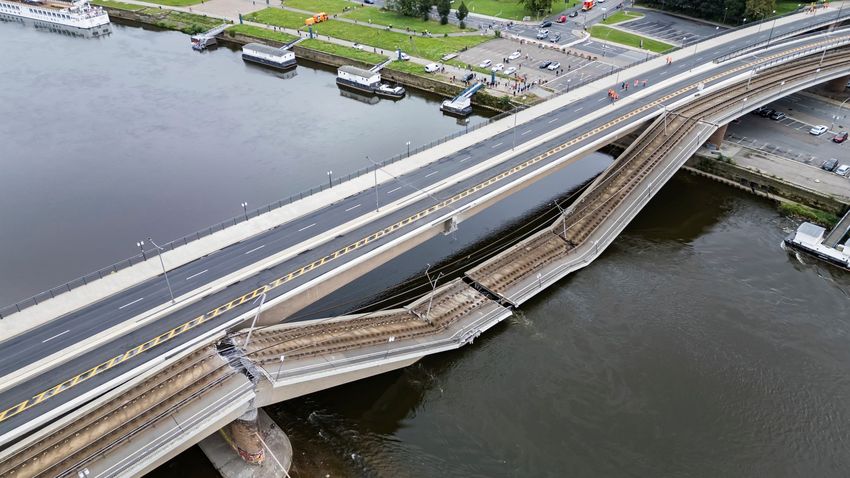
CHAIN SURVEYING
Chain survey is suitable in the following cases: (i) Area to be surveyed is comparatively…
Posted inSurveying
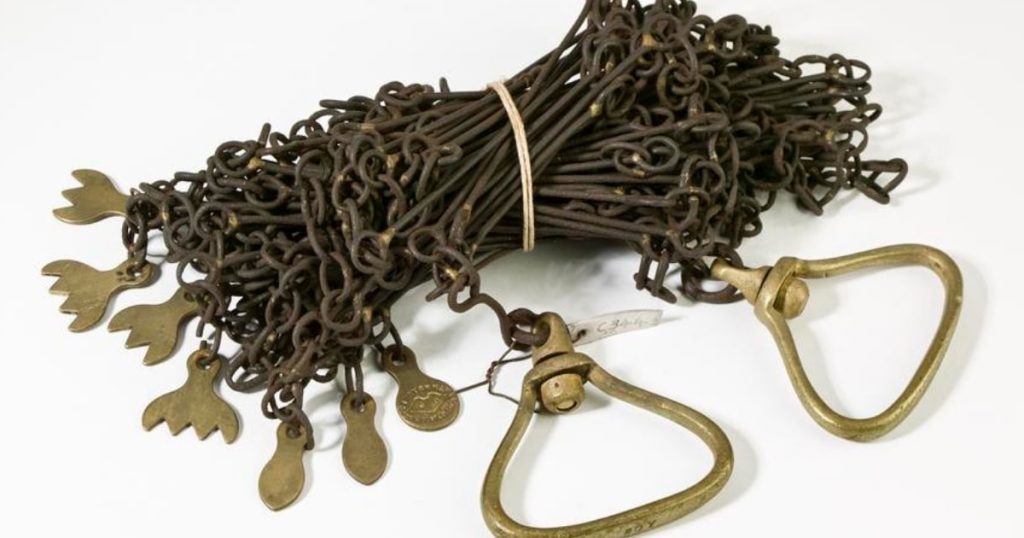
INSTRUMENTS USED IN CHAINING
The following instruments are required for measurements with chain and tape: (i) Arrows (ii) Pegs…
Posted inSurveying
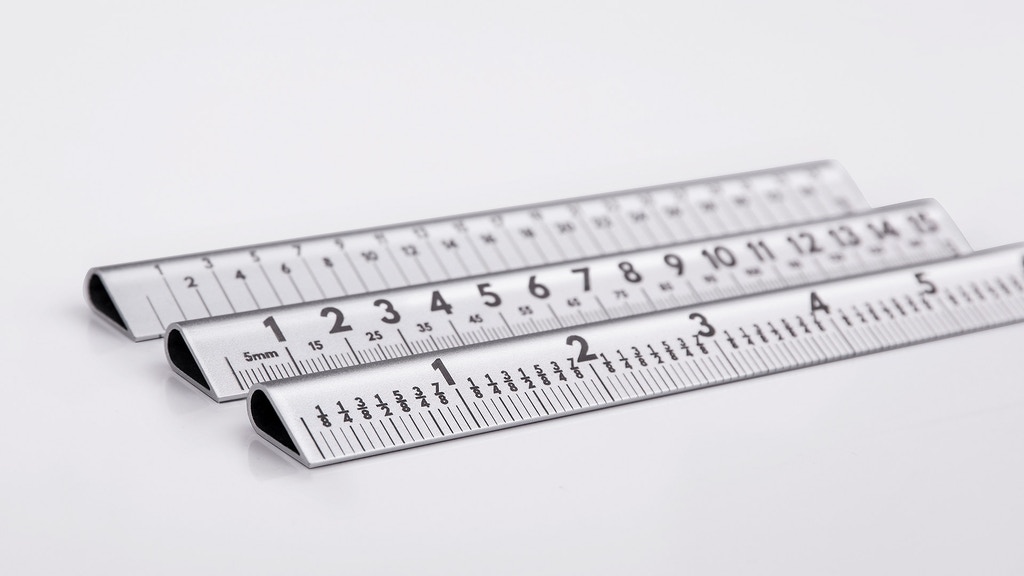
Measurement with Chains or Tapes
Measurement of distances using chain or tape is termed as chaining. This is the accurate…
Posted inSurveying
Linear Measurements and Chain Surveying
All the distances required for making a plan are the horizontal distances. Hence in the…
Posted inSurveying
UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS
In 1960 System International (SI units) unit was approved by the conference of weights and…
Posted inSurveying
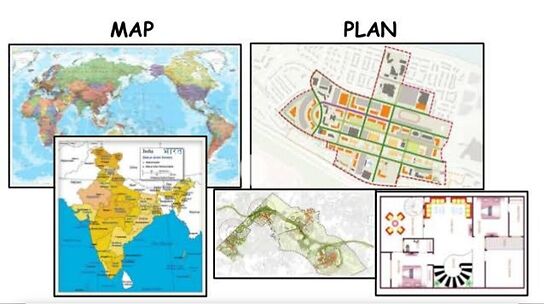
PLANS AND MAPS
As stated in the definition of surveying the objective of measurements is to show relative…